Keywords
|
| Environment, Health and Safety (EHS), Behaviour Based Safety (BBS), International Labour Organization (ILO), Occupational Health EHS Assessment Series (OHSAS) |
INTRODUCTION
|
| An organization at this stage of the journey in developing a Proactive EHS culture has adopted the idea of continuous improvement and applied the concept to EHS performance. There is a strong emphasis on communications, training, management style, and improving efficiency and effectiveness. Everyone in the organization contributes for EHS Culture Progress is made one step at a time and never stops. |
| - The organization begins to act strategically with a focus on the longer term as well as awareness of the present. It anticipates problems and deals with their causes before they happen. |
| - Decisions are made in the full knowledge of their EHS impact on work or business processes as well as on departments and functions. |
| - Management’s role is seen as coaching people to improve business performance |
| - Employees are aware of work or business processes in the organization and help managers to manage them. |
| - There is no goal conflict between EHS and productivity performance. EHS and productivity are seen as interdependent. |
| - Employees recognize and state the need for collaboration between departments and functions. They receive management support, recognition and the resources they need for collaborative work. |
| - Mistakes are viewed in terms of work process variability. |
| - Learning from others both inside and outside the organization is valued. Time is made available and devoted to adapting such knowledge to improve business performance. |
| - Collaborative relationships are developed between the organization and regulators, suppliers, customers and contractors. |
| - Short term performance is measured and analyses so that changes can be made which improves long term performance. |
| - The relationship between management and employees is respectful and supportive. Employees are respected and valued for their contribution. The organization rewards not only those who ‘produce’ but also those who support the work of others. Rewards are given for improving processes as well as results. |
| - Management and employees are aware of the impact of cultural issues, and these factors are considered in key decisions. Management strongly believes that EHS Culture is part of the business and enhances the Profitability. |
| - Value learning from other organizations and establish systems for doing this. They recognize the effects of processes on EHS results. |
| - Review EHS targets and objectives. They remain alert to potential EHS improvements. |
| - Provide help to suppliers and contractors to improve their EHS performance. |
| - Introduce organizational cultural indicators (e.g. standards of housekeeping, reporting of ‘near misses’) that have a bearing on EHS performance. |
| - Make comparisons with external organizations chosen as benchmarks. |
| - Transparent communication with the public on EHS issues. |
| - Encourage employees to assist in the further improvement of existing processes. |
| Top management support for EHS culture, providing resources for incident investigations, and EHS training helps in establishing the best EHS culture. Further progress toward a true EHS culture uses accountability systems. These systems establish EHS goals, measure EHS activities, and charge costs back to the units that incur them. Ultimately, EHS becomes everyone’s responsibility, not just the EHS director’s. EHS becomes a value of the organization and is an integral part of operations. Management and employees are committed and involved in preventing losses. Over time the norms and beliefs of the organization shift focus from eliminating hazards to eliminating unsafe behaviors and building systems that proactively improve Environment, Health and Safety conditions. Employee EHS and doing something the right way takes superiority over short term productivity pressures. Simultaneously, productivity does not suffer but is enhanced due to the level of excellence developed within the organization. |
| The summary of research article further, emerged in the following areas: |
| - Proactive and Generative culture is increasing trend. |
| - Works environment improves which in turn improves the productivity.’ |
| - The EHS performance is improved year after year. |
Methodology
|
Theoretical framework
|
| The existing EHS theories / Models have been taken as reference to carry out the Research work. These theories have been put into practice and new EHS-Culture Evaluation Model has been developed through the EHS Evaluation Software. |
| These R& D efforts involving evaluating and improving employee EHS-Culture should result in high employee morale and productivity. |
Source Data
|
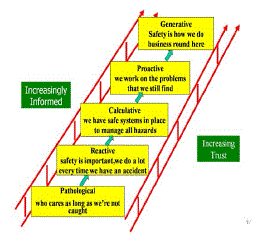
| The source data are collected through the employee’s interaction by set a of questions which qualifies their extrinsic/Intrinsic/General Satisfaction about the job engagement. Survey worldwide research done on EHS-Culture, especially quantification of EHS-Culture under globally recognized levels of Pathological, Reactive, Calculative, Proactive and Generative. |
| Developed a Proforma Questionnaire, with specific Indian context and culture, to determine existing EHS-Culture. To develop an advanced software to quantitatively evaluate existing EHS-Culture in an EHS goals, measure EHS activities, and charge costs back to the units that incur them. Ultimately, EHS becomes everyone’s responsibility, not just the EHS director’s. EHS becomes a value of the organization and is an integral part of operations. Management and employees are committed and involved in preventing losses. Over time the norms and beliefs of the organization shift focus from eliminating hazards to eliminating unsafe behaviors and building systems that proactively improve Environment, Health and Safety conditions. Simultaneously, productivity does not suffer but is enhanced due to the level of excellence developed within the organization. |
Methodology
|
Theoretical framework
|
| The existing EHS theories / Models have been taken as reference to carry out the Research work. These theories have been put into practice and new EHS-Culture Evaluation Model has been developed through the EHS Evaluation Software. |
| These R & D efforts involving evaluating and improving employee EHS-Culture should result in high employee morale and productivity. |
Source Data
|
| The source data are collected through the employee’s interaction by set of questions which qualifies their extrinsic / Intrinsic / General Satisfaction about the job engagement. Survey worldwide research done on EHS-Culture, especially quantification of EHS-Culture under globally recognized levels of Pathological, Reactive, Calculative, Proactive, Generative. |
| Developed a Proforma Questionnaire, with specific Indian context and culture, to determine existing EHS-Culture. To develop an advanced software to quantitatively evaluate existing EHS-Culture in an Industry. |
| Collected data by interviewing 500 number of employees of the Industry and contractors and record data in the standardized questionnaire. |
Sampling
|
| The sampling includes the collection of EHS - Culture data from same level of employees at shop-floor through the questions developed to suit the Indian context. These answered questions will be analyzed through the advanced EHS Software Product. |
Statistical Tools
|
Instruments
|
| a. EHS – Culture Software Product |
| b. Questionnaire |
Data generation through the Software
|
| a. Survey worldwide research done on EHS-Culture, specially quantification of EHS-Culture under globally recognized levels of Pathological, Reactive, Calculative, Proactive, Generative. |
| b. Developed a Proforma Questionnaire, with specific Indian context and culture, to determine existing EHS-Culture including the Technical Data Analysis. |
| c. Developed an advanced software to quantitatively evaluate existing EHS-Culture in an Industry. |
| d. Collected data by interviewing all employees of the Industry and contractors and record technical data and improve to meet the international standards OHSAS. |
| e. Entering data in the Software developed. |
| f. Obtaining results of the vast data by the Software, analyzing the results, interpreting and determining strengths and weaknesses in EHS-Culture with respect to technical data analysis. |
| g. Developed an effective program to improve weak areas in EHS-Culture. |
Objective Methodology of Research
|
Objectives
|
| Quantified and Evaluate EHS-Culture in an industrial set up covering Top down the hierarchy and including the contract employees through the EHS Software & works environment study and determine the strength and weakness to evolve the EHS - Culture improvement plan. |
Causes of Industrial Incidents
|
| Industrial Incidents are invariably caused due to Unsafe Acts (USAs) and Unsafe Conditions (USCs). There are 9-Categories of Heinrich’s Unsafe Acts and Unsafe Conditions at works. Though the technology is advanced, the human Attitude and Behavior is not coping with the industrial hazards. The frequency / severity of the Incidents are not clearly and reliably controllable due to either lack of awareness by employees and mainly due to the typical Indian “Chalta Hai Culture. |
Control and Minimization of Incidents
|
| Incidents can be minimized / controlled by changing the human behavior through training and retraining programs and control of an adaptation to stress conditions. |
| Unsafe Acts and Unsafe Conditions can be minimized by controlling the 9-Catagories of Heinrich’s list through special training and special inspection and control of Unsafe Conditions of Plant and machinery, tools and tackles. |
| Finding the poor EHS culture of employees using the advance EHS Software and training the employees to change their behaviour which in turn brings about the Proactive and Generative EHS culture. |
EHS Culture
|
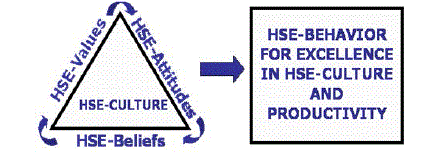
| Shared values ( what is important) and beliefs ( how things work) that interact with an organizations structure and control systems to produce behavioural norms ( the way we do things around here). |
A Peep in to EHS-Culture for EHS and Productivity
|
| We have defined EHS-Culture as a composite of our Values, Beliefs and Attitudes. Let us look at EHS-Culture through a graphic presentation: |
Essentially EHS-Culture depends on the following basic parameters
|
Employee Engagement
|
| Engagement is how deeply an employee is “Engaged” in his organization, his work and his colleagues i.e. Commitment to his organization, his work and his colleagues. Employee Engagement is a new concept now for quantifying and evaluating employee EHS-Culture. |
Employee satisfaction
|
Employee satisfaction has three parameters
|
| a. Intrinsic Satisfaction: This is how intrinsically the employee likes his work, |
| b. Extrinsic Satisfaction: This is how the employee is satisfied with the facilities, powers, recognition, growth opportunities are provided, |
| c. General satisfaction: Comes from standing of the organization where he works, in regard to growth, competition etc. of the organization. |
| Basically, the Incidents are caused due to unsafe acts and unsafe conditions. The EHS Culture Evaluation eliminates the unsafe condition and unsafe acts. |
| There is a scope for improving the EHS culture in M/s JSW Steel Limited. |
Evaluation
|
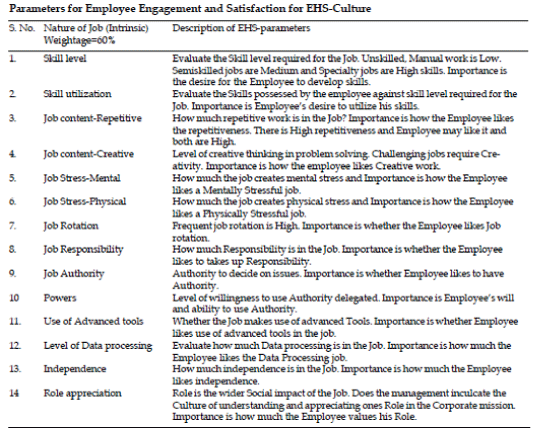
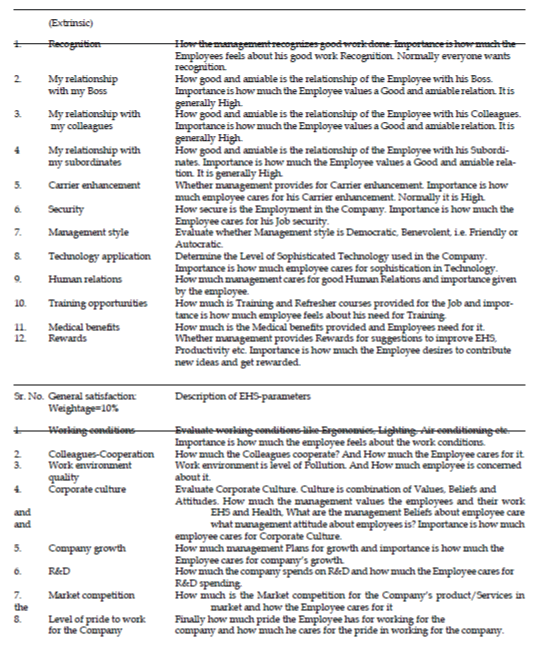
| The following Table gives a series of parameters covering Intrinsic, Extrinsic and General EHS-Culture parameters that govern Employee Engagement and Job satisfaction levels that need to be quantified and evaluated, analyzed and understood for developing a sustainable long term EHS-Culture for EHS-Excellence and productivity: |
| The questionnaires filled by the employees provides an overview of the concepts that integrate in to EHS-Culture for individuals, Groups and the Corporate system as a whole. The proposed Research shall work in to these overall concepts on EHS-Culture and arrived at a uniquely new type of EHS-Culture quantification and evaluation to develop an improvement plan for an industrial complex. |
Data Collection
|
| The Data collection includes the collection of EHSCulture data from same level of employees at shopfloor through the questions developed to suit the Indian context. These answered questions will be analyzed through the advanced EHS-Culture Software Module developed conforming to International Standards. |
Software and Physical Tools
|
| Obtaining results of the vast data by the Software applications, analyzing the results, interpreting and determining strengths and weaknesses in EHS-Culture with respect to technical data analysis. |
| To develop an effective program to improve weak areas in EHS-Culture and to reduce works environment levels to acceptable standards. |
 |
| a. EHS – Culture Software application results. |
| b. Obtaining results of the vast data by the Software applications, analyzing the results, interpreting and determining strengths and weaknesses in EHS-Culture with respect to technical data analysis. |
| The following shop-floor employees have been considered for EHs evaluation. |
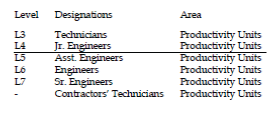 |
General idea about EHS-Culture
|
| EHS-Culture is now recognized as progressing from Pathological to Reactive to Calculative to Proactive to finally Generative. Following table illustrates the concept and meaning of these stages of EHS-Culture evolution: |
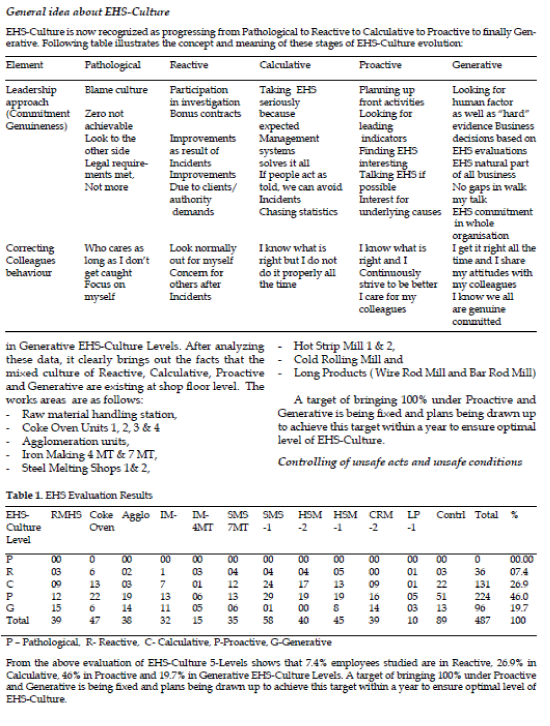 |
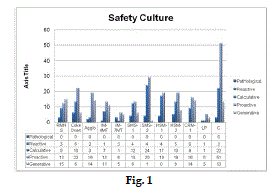
| From the above evaluation of EHS-Culture 5-Levels shows that 7.4% employees studied are in Reactive, 26.9% in Calculative, 46% in Proactive and 19.7% in Generative EHS-Culture Levels. A target of bringing 100% under Proactive and Generative is being fixed and plans being drawn up to achieve this target within a year to ensure optimal level of EHS-Culture. |
| 96% of Injuries are caused because of unsafe acts of employees in industrial sectors. The unsafe acts are violations of rules, procedures, standards, standard operating procedures, wrong designing the layout by the engineers. It is therefore, important to control and eliminate the unsafe acts which in turn built up the better EHS culture in an organization. |
Unsafe Act: A conduct (whether witnessed or not) that
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| • Unnecessarily increases the likelihood of injury, if not corrected |
| • Violates established EHS rules/procedures or un written rules of common sense and good judgment |
| • May not have been previously recognized as pre senting injury potential |
Unsafe Condition: Is a condition that may be caused by
|
| • The action or inaction of employees in any area that may lead to an incident or injury, if uncorrected. |
| • Faulty design, incorrect fabrication or construction, or inadequate maintenance and subsequent deterioration. |
| Contd........... The unsafe acts and unsafe conditions are the foundation for the serious injuries. Hence, it is essential to eliminate the unsafe acts of the employees at works site. The total elimination of unsafe acts and unsafe conditions at works site will built up the strong EHS culture. |
Unsafe Acts and Unsafe Conditions
|
| • The key point that differentiates unsafe conditions from unsafe acts is that unsafe conditions are normally beyond the direct control of employees in the area where the condition is observed. |
How to eliminate the unsafe acts and unsafe conditions at works site?
|
| • Daily EHS observations at works site to find out unsafe acts of the employees. |
| • What energy hazards are present? |
| • Are employees aware of the hazards? |
| • Are primary & secondary controls in place for each task? |
| • What training/knowledge is needed to do the task safely? |
| • Is there a work/EHS plan for the task? Is it followed? |
| • Personal Protective Equipment – Is it properly used? |
| • What are the positional hazards & risks? Is protection in place? |
| • What are the ergonomic issues (posture, lifting, lighting, noise, repetitive motion, etc.)? What protection is in place? |
| • Tools & Equipment problems – Right tools used? Are tools in safe condition? Are tools properly used? |
| • What EHS procedures apply to each task? |
| • Procedures – Are they up to date, known, understood, practiced? |
| • Is housekeeping good? Trends? |
Ways to reduce Incidents:
|
| • By ensuring that all employees are competently trained to do their work. |
| • Identifying hazards in the job. |
| • Assessing the risks from the hazards. |
| • Managing the risk. |
Controlling risk behaviour
|
| Employees take calculated risk because of their complacent and long working services. The common and simple examples of risk behavior are working on energized equipment without electrical isolation. Working at Height without anchoring the hook of the full harness belt. Over speeding of vehicles on road. Speed Thrills, but it Kills. |
Training Programs
|
| To improve the EHS culture in the organization, the following training programs have been conducted for employees to raise their cultural levels. |
| - EHS Induction for new recruits |
| - Holistic approach for EHS Management |
| - Permit to Work and Protocol |
| - Road EHS Measures |
| - Working at Height |
| - Confined Space Entry |
| - Lock Out and Tag Out |
| - EHS Model |
Comparing EHS Performance at the time of evaluating existing EHS culture and after bringing in improvements among employees requiring EHS improvement
|
| The EHS Culture valuation has been carried out for two successive years. The first year is taken as base line assessment of EHS Culture. The various EHS concerned activities such as Training Program, improvement works area, counseling and coaching of workforce and improving the personal protective equipment at site have been taken up for improvement. |
| From the above evaluation of EHS-Culture 5-Levels shows that 6.2% employees studied are in Reactive, 23.30 % in Calculative, 45 % in Proactive and 25.5v% in Generative EHS-Culture Levels. |
| There is reduction in percentage of EHS culture level in Reactive and Calculative and Proactive EHS cultural level is more or less same. The Generative culture level is well improved. |
| A target of bringing 100% under Proactive and Generative is being fixed and plans being drawn up to achieve this target within two years to ensure optimal level of EHS-Culture. |
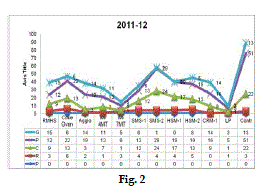
| Reportable Injury: Employee is not in a position to report duty within 48 hours after the injury. |
| FR:Frequency Rate: Number of Reportable injuries per Million Man Hours worked. |
| IR: Incident Rate: Number of Reportable injuries per 1000 employees. |
| From the above graph, it shows that there is marginal improvement in Frequency Rate and Incident Rate every year. |
Recommendations
|
| The following suggestions are made to Management for improving the EHS Standards. |
| 1. Senior leaders must “walk the talk” |
| 2. Hold leaders accountable |
| 3. Add the individuals compliance to their performance review |
| 4. Deepen our observation skills beyond the obvious PPE |
| 5. Get serious about PPE! |
| 6. Analyze the data to understand systemic issues- for instance which procedures are regularly being violated |
| 7. Monitor close out of potential serious / fatal cor- rections- set expectations of rapid response and escalate weekly report of outstanding actions to Management. |
| 8. Incident reporting has to increase dramatically |
| 9. Understand of importance of near misses and promote reporting in all Divisions |
| 10. Accelerate Incident Investigation Standard training |
| 11. Which EHS Observations should also be recorded as incidents - only then will we analyze root cause and employ systemic corrections |
| 12. Senior leaders to ask questions about reporting and investigation rate at management meetings |
| 13. Line managers to review quality of the investigation |
EHS Action Plan
|
| The following EHS Action Plan is scheduled to control the injuries. |
| 1. Encouraging to report Near Miss Incidents. |
| 2. Toolbox Talk before starting the job |
| 3. Daily EHS Observations at Works & Construc- tion Sites |
| 4. EHS Culture Training Programs |
| 5. Improving the quality of Personal Protective Equipment. |
| 6. Enforcement of Permit to Work and EHS Measures |
| 7. Developing EHS Observations Matrics |
| 8. Conducting the EHS Action Meeting |
| 9. Incident Investigation and corrective measures across the organization. |
| 10. Periodical medical examination for employees to ascertain their physical fitness. |
Conclusion
|
| The research work on “Quantification and Evaluation of Environment, Health and EHS (EHS) culture and development of improvement plan for industries leads to the following major conclusions: |
| 1. Based on the study carried out on EHS evaluation for shop floor employees including contractors, the EHS culture can be quantified from lower level to higher level on a ladder of 5 steps namely; Pathological, Reactive, Calculative, Proactive and Generative. In the present study, substantial improvement was achieved in converting the lower level culture to higher level culture after quantification. |
| 2. By evaluating the EHS culture using of EHS Software, poor EHS culture employees can be identified and which in turn may help us to draw the road map for them in improving the EHS culture through EHS Training Programs and also imparting on-line job training at work. In the present study this approach shows significant improvement in achieving the proactive and generative culture which meets the world class standards. |
| 3. The research concludes that the methodology used for evaluating and improving the EHS Culture is strongly recommended for other Industrial Sectors too to achieve world class level EHS culture. |
| 4. The methodology used for identifying the cultural values helps in understanding the present organization culture level and also helps in measuring the weakness regarding EHS Culture. |
| 5. A software for quantitative evaluation of existing EHS-Culture in an Industry and a Hygiene Index Software conforming to ILO-Model is developed and the model is successfully validated using the surveyed data. |
Tables at a glance
|
|
|
| |
Figures at a glance
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
Figure 5 |
|
References
|
- Clarke, S. 1999. Perceptions of Organizations EHS: Implications for the development of EHS Culture.
- Health and EHS Executive 2005. A review of EHS Culture for the development of the EHS culture inspection toolkit. Human Engineering Shore House, Bristol. Research Report 376.
- Javis, M. and Tint, P. 2009. The formation of good EHS culture at the enterprise. Journal of Business Economicsand Management. 10 (2) : 169-180.
|