The present paper deals with the observation on physico-chemical characteristics of river Saryu that was found polluted by various sources of pollution. River Saryu is regarded as fresh perennial water body which was observed regularly polluted by discharge of different physical and chemical pollutants released from various small scale industries like rice mills, petroleum workshops, railway workshops, dairy, laundries and cereal market. Pollutants discharged from these sources were found resulting into deterioration of water quality and disturbing the aquatic ecological balance of river Saryu.
Keywords |
| Ayodhya, Faizabad, Physico-chemical parameters, Water quality |
INTRODUCTION |
| Water being a universal solvent has been and is being utilized by mankind. Of
the total amount of global water, only 2.4% is distributed on the main land, of
which only a small portion can be utilized as fresh water. The available fresh
water to man is hardly 0.3-0.5% of the total water available on the earth and
therefore, its judicious use is imperative (Ganesh & Kale, 1995). The fresh
water is a finite and limited resource (Bower, 2000). The utilization of water
from ages has led to its over exploitation coupled with the growing population
along with improved standards of living as a consequence of technological
innovations (Todd, 1995 and Raj, 2000). This contamination of river water
body is not away from the evils of modernization. |
| In Uttar Pradesh the twin cities Ayodhya and Faizabad are famous lor
their historical background. A fresh perennial water body known as Saryu River is running along both the cities. River Saryu is well known as a major
source of water required for various purposes of domestic, agricultural and
commercial utilization. On the entrance, this water body gets contaminated
by the wastes discharged from different small-scale industries like rice mills,
petroleum workshops, railway workshops, dairy, laundries and cereal market.
Garbage from domestic sources, hospitals and pathological labs were
also found discharged into river Saryu. Over all these municipal wastes are
responsible for the deterioration of water quality of river Saryu. |
| The present study deals with pysico-chemical characteristics of river water
quality of Saryu contaminated by different types of municipal wastes. |
Materials and Methods |
| Municipal wastcwater samples were collected from five prefixed sampling
sites on the major drains (viz. Dl, D2, D3, D4 and D5) of city. The samples
were brought to laboratory and analyzed for the selected parameters using the
standards methods (Trivedi and Goel, 1984; APHA, 1992) while pH and Dissolved
Oxygen (DO) were measured on the spot of collection of samples. The
other parameters were analyzed in the laboratory within twenty-four hours. |
Result and Discussion |
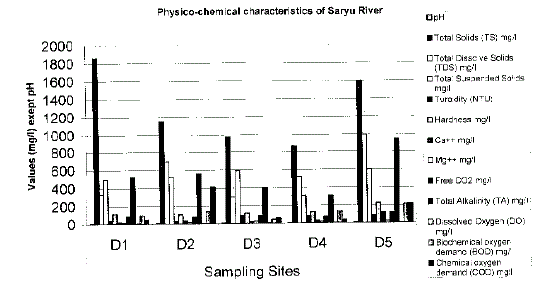
| The values of selected physico-chemical parameters of river Saryu at selected
sites viz. Dl, D2, D3, D4 and D5 have been shown in Table 1. |
| Table 1 reveals that the water was found alkaline as pH values fluctuates
between 7.5-7.7 excluding the site D5 that was recorded 6.0. This fluctuation
seems to be due to dilution of industrial and sewage effluents in rainy season.
Increased pH surface water is obliviously related to metabolic activities of
autotrophs, which by utilizaing CO2 during photosynthesis reduces hydrogen
ion concentration. The similar observation was reported by Gupta and Sharma
(1994), Singh (1996), Chandra and Sharma (2000). Some other parameters like
hardness vs. total dissolve solids (TDS) and turbidity vs total suspended solids
(TSS) showed little relation among them. It is provably due to heavy burden
of over population, increased sewage disposal and other human activities like
washing, bathing, throwing of dead bodies and carcasses. Dissolve Oxygen
(DO) was found from 2.07-6.60 mg/L, however, BOD values were recorded
from 44.5-214.6 mg/L. The low values of DO might be due to higher growth
of bacteria, which utilize oxygen for their metabolic activities as reported by
Roy et al. (1984), Badge and Vcrma (1985). The maximum chemical oxygen
demand (COD) value of 452 mg/L was observed at Dl. COD values have been
found to be much higher than BOD values which were due to presence of
chemically oxidisable carbonaceous matter as well as inorganic matters like
nitrates, sulphides and reduced metal ions coming from industrial effluents,
washing, bathing (detergents and soap) and other activities. Rana, 1997; Prasad
and Saxcna, 1980 and Gunalc, 1991, have reported the same observations. It
would be apparent from an examination of Table 1, that water quality of river
Saryu has undergone a remarkable change, which may directly be attributed to increase in industrial units and population of the cities (Ayodhya and Faizabad).
Increased human interferences may be caused deterioration of water
quality of river Saryu. |
 |
| |
Tables at a glance |
 |
| Table 1 |
|
| |
References |
- APHA, AWWA, WPCF, 1992. Standard Method for Examination of Water Wastewatcr, 18th Edition, U.S.A.
- Badge, U.S. and Verma A.K. 1985. Limnological study of J.N.U. lake, New Lucknow. India. Proc., National Symposium Pure and ApplLimnol.32 : 16-23.
- Bower, H. 2000. Integrated Water Mangement : Emerging Issue and Challenges, Agricultural Water Management.
- Chandra, R.R., Bahadur, Y. and Sharma B.K. 2000. Physico-chemical studies on river Ganga and its tributaries in Uttar Pradesh in present status.In :Pollulion and Biomonitoring of Indian River, eds. R.K. Trivey, ABD Publisher, Jaipur (India) 275-280.
- Ganesh, R. Hegde and Kale, Y.S. 1995. Quality of lentic waters of Dharwad district in northKamataka. Ind. J. Env.Hlth. 37 (1) : 52-56.
- Gunale, V.R. 1991. Algal communities as Indicators of pollution. J. Environ. Biol. 12 : 223-232.
- Gupta, M.C. and Sharama, L.L. 1994. Variation in selected limnological parameters ofAmarchand reservoir, southern Rajasthan. Poll.Res. 13 : 217-222.
- Prasad., B.N. and Saxena, M. 1980. Ecological study of Blue green algae in river Gomati. Indian J. Environ. Hit. 22 : 151-158.
- Rana, B.C. 1977. Algae of sugar factory waste. Geobios. 4 : 121
- Roy Dutta, Marity S., Dutta, B.R. and Banerjee, R.D. 1984. Environment and Ecology. 2 : 87-90.
- Sinha, A.K., Vajpayee P., Kumar A., Singh, R.P. and Pandey, D.P. 1985. Water quality of river Sai at Rae-Bareli preliminiarry report. Res. J. P I. Environ. 2 : 87-90.
- Singh, V.P. 1996. Studies on river Sai with special reference to its aquatic flora (Ph.D. Thesis) C.S.J.M. Universit, Kanpur.
- Todd, D.K. 1995. Groundwater hydrology. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
- Trivedy, R.K. and Goel P.K. 1984. Chemical and Biological Methods for Water Pollution Studie, Environ, Publ.Karad, (Maharashtra)
|